Handheld fiber laser welding machine video
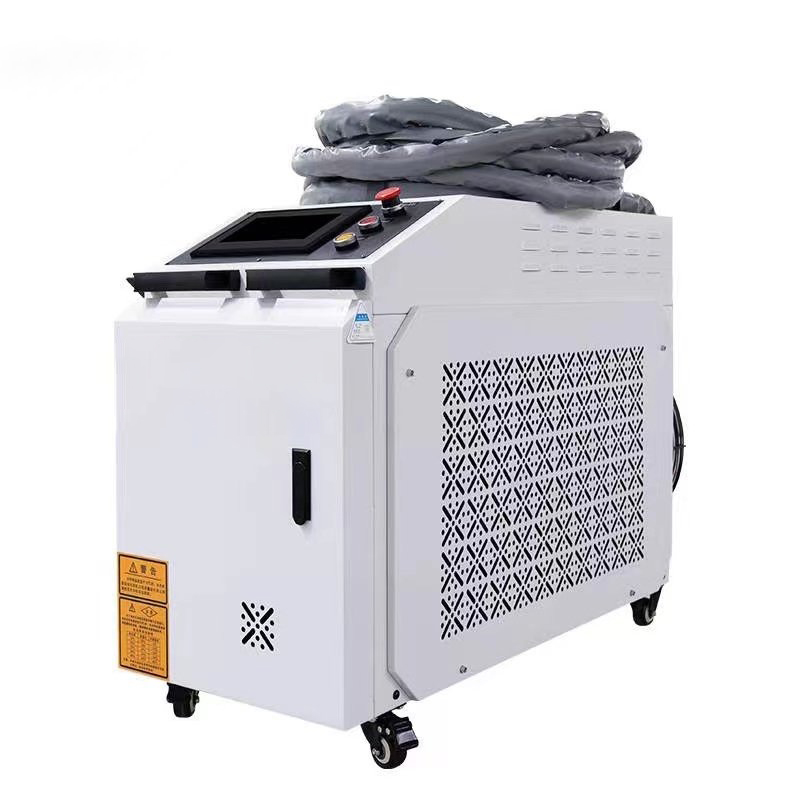
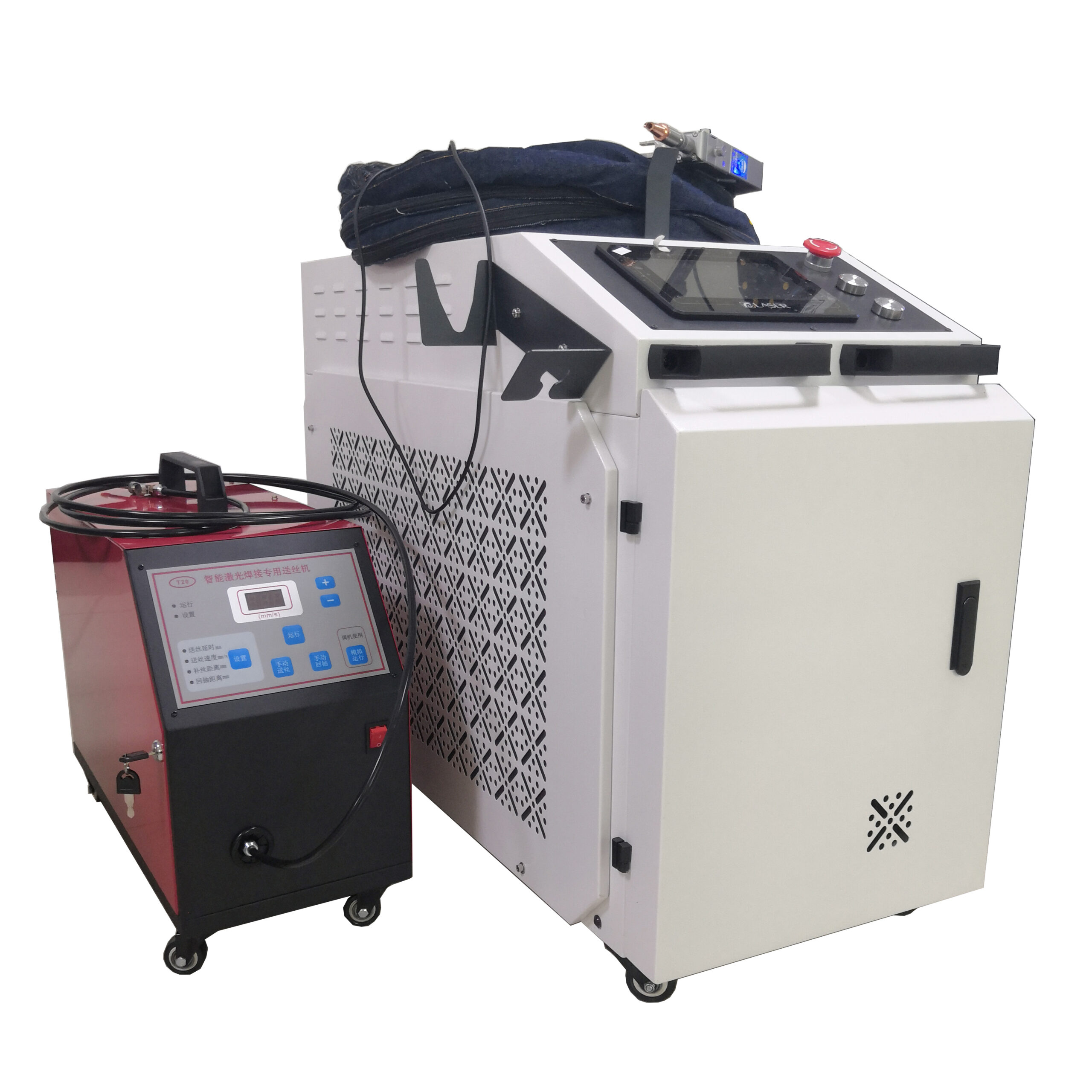
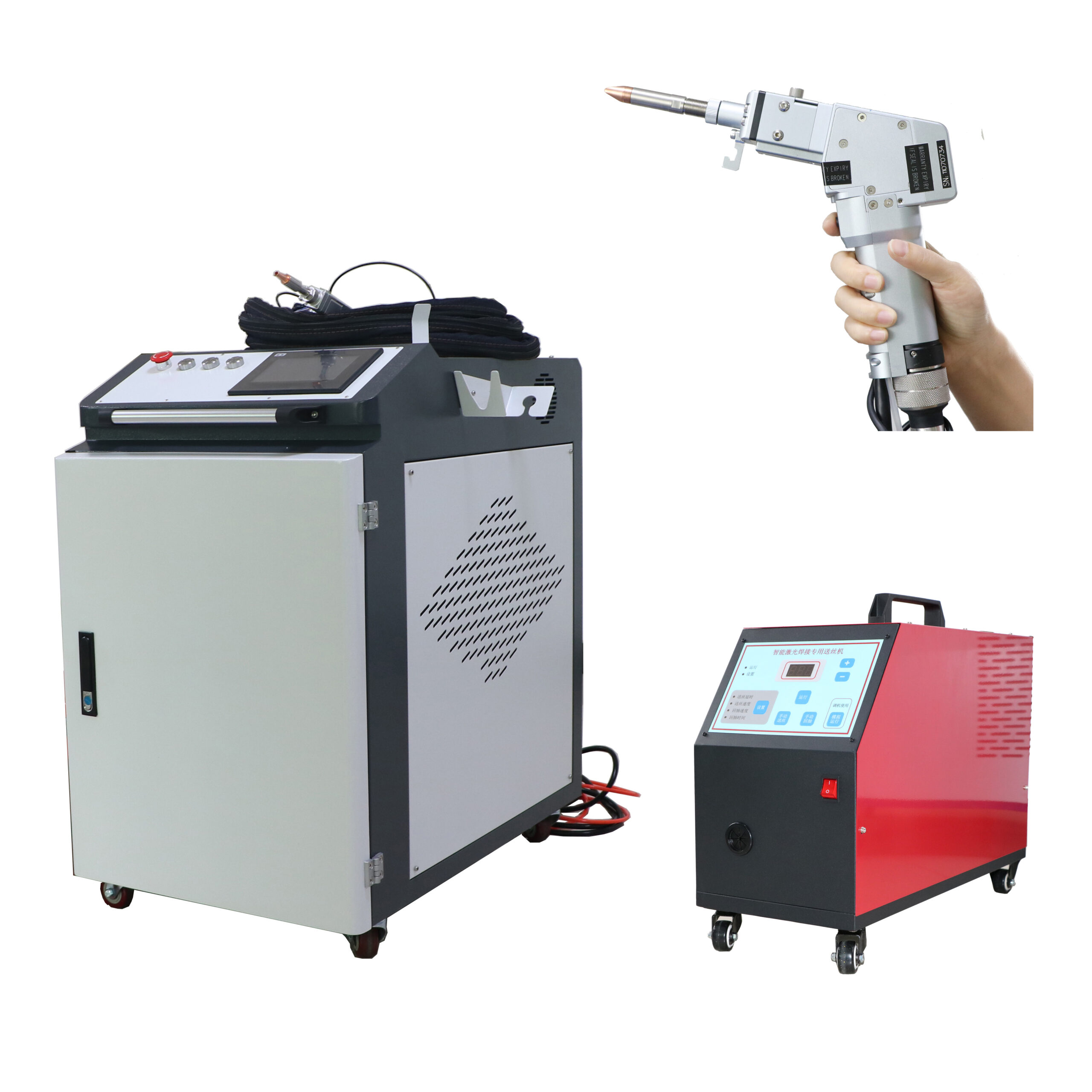
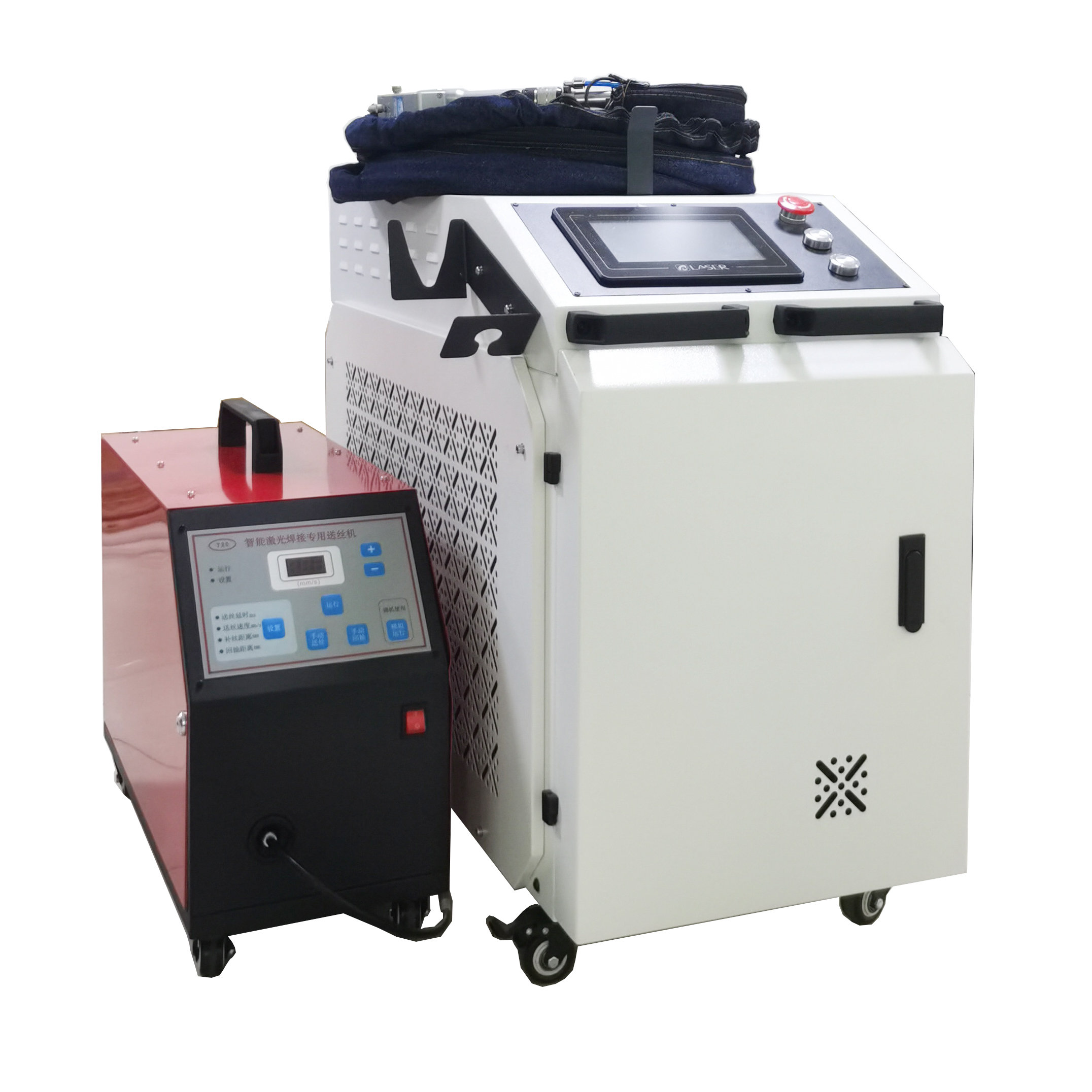
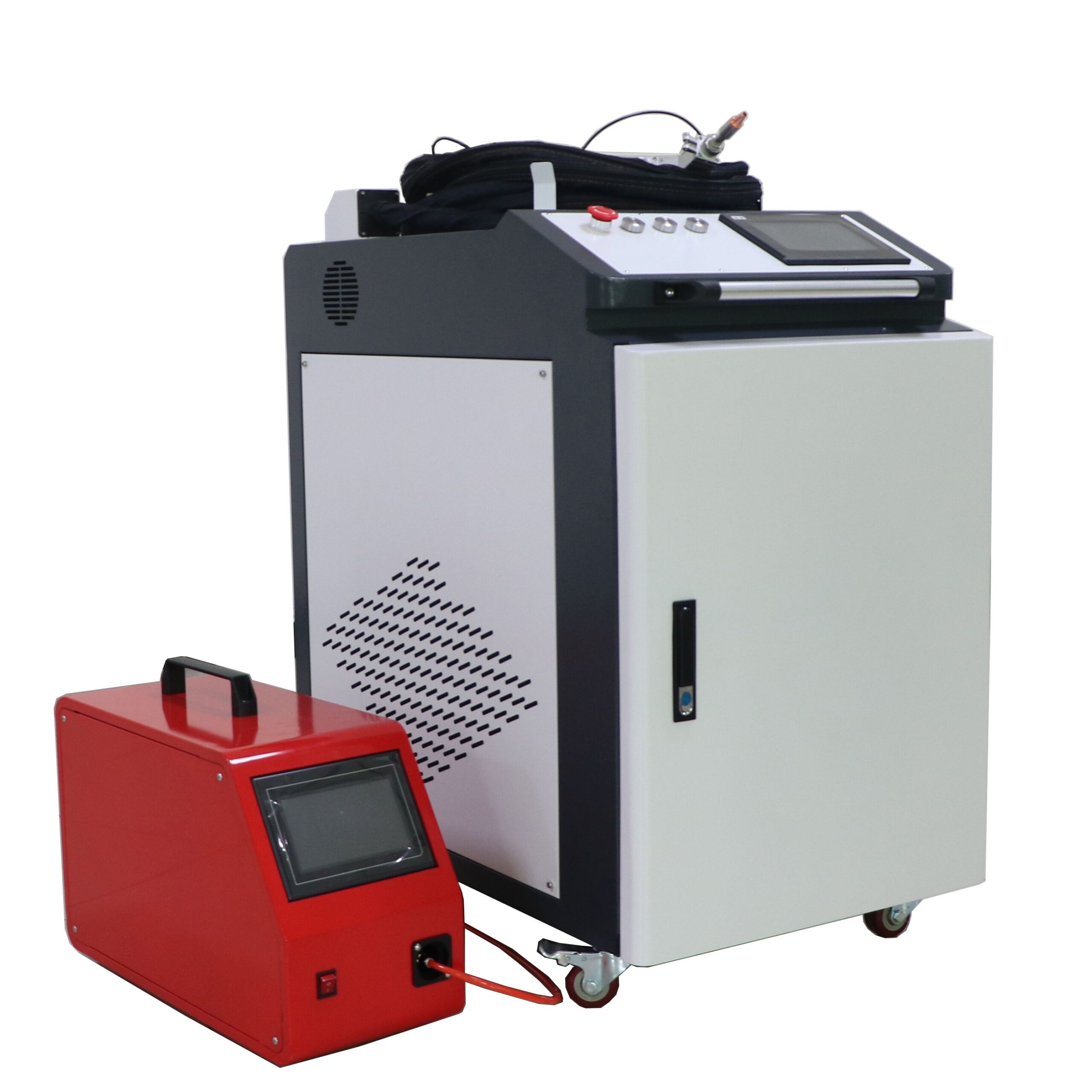
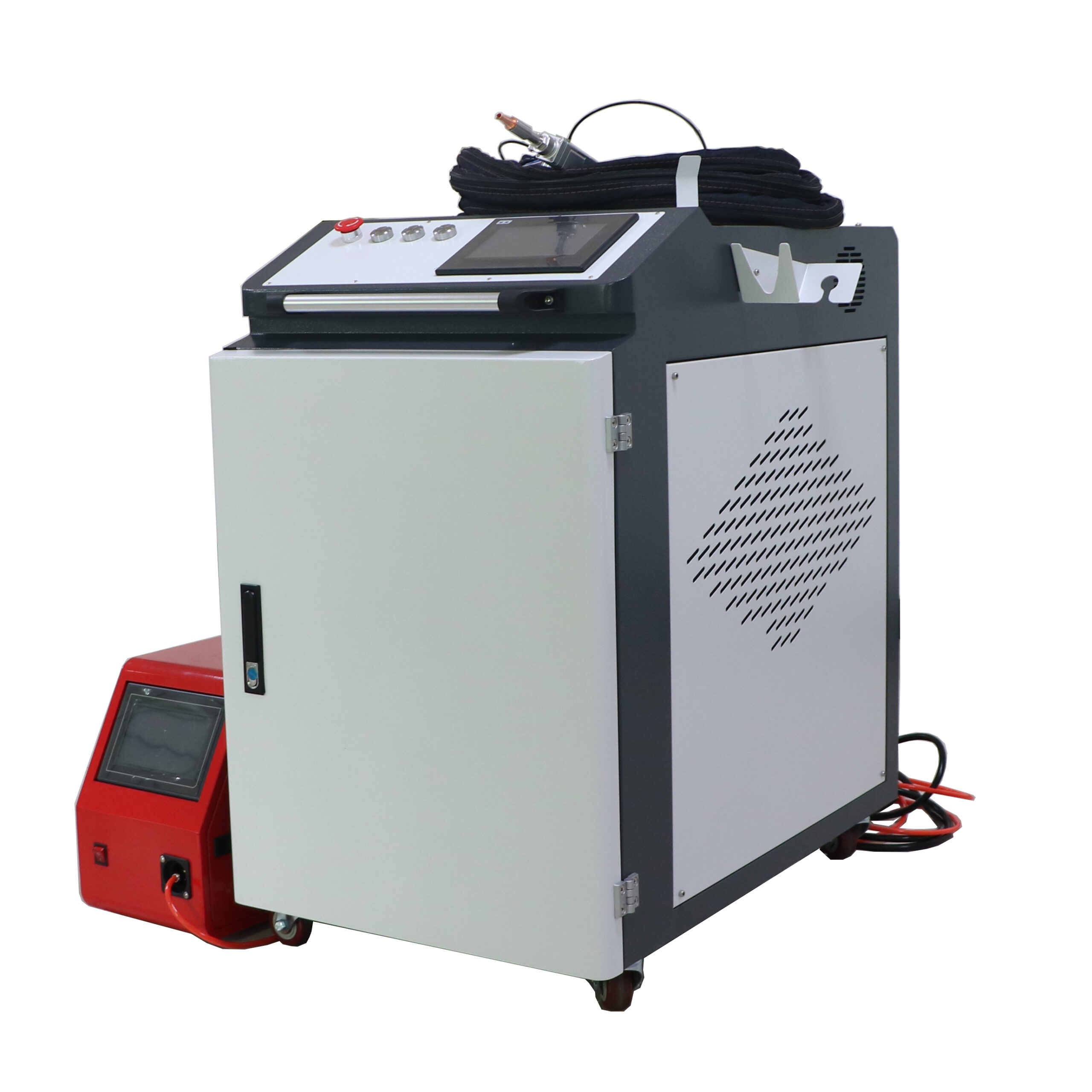
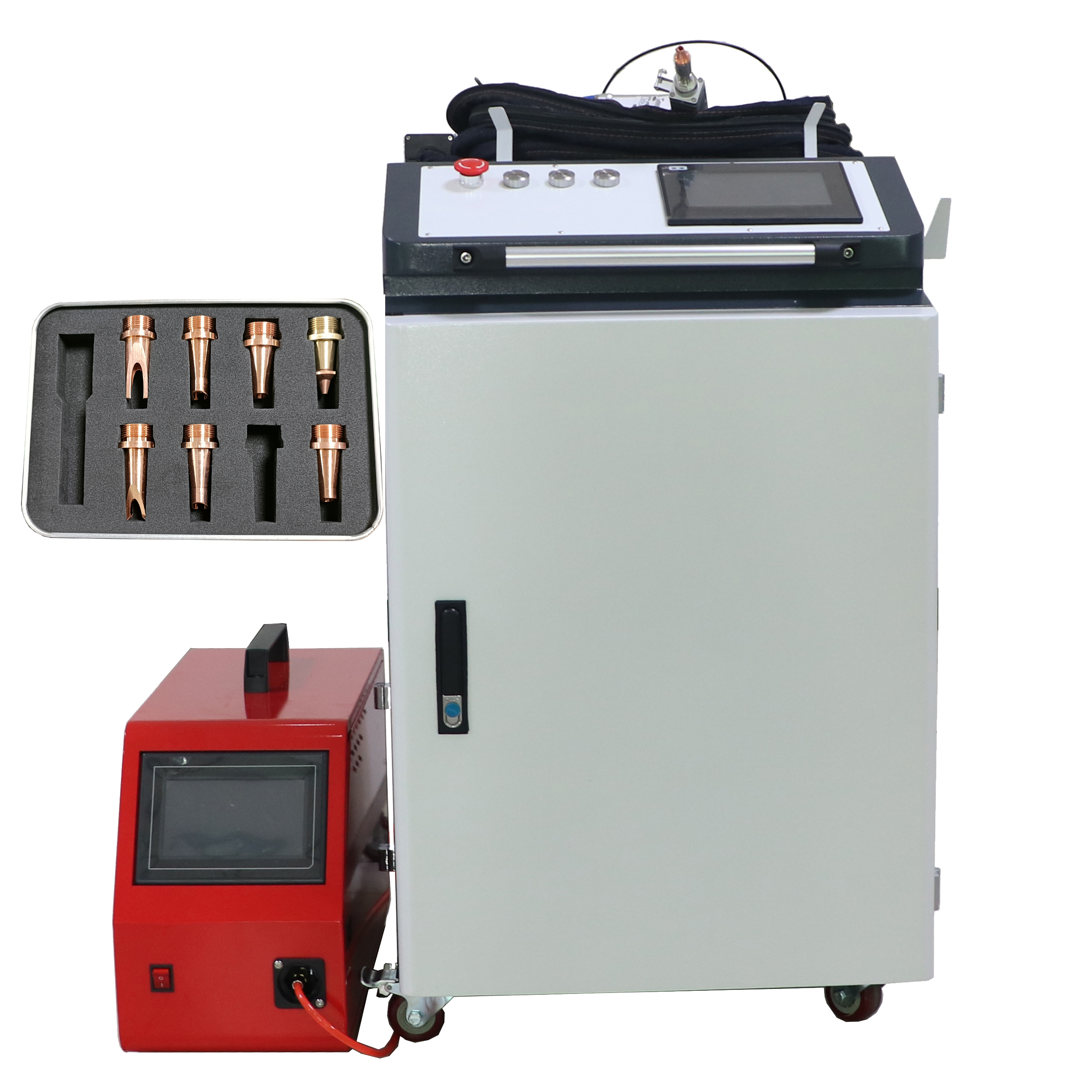
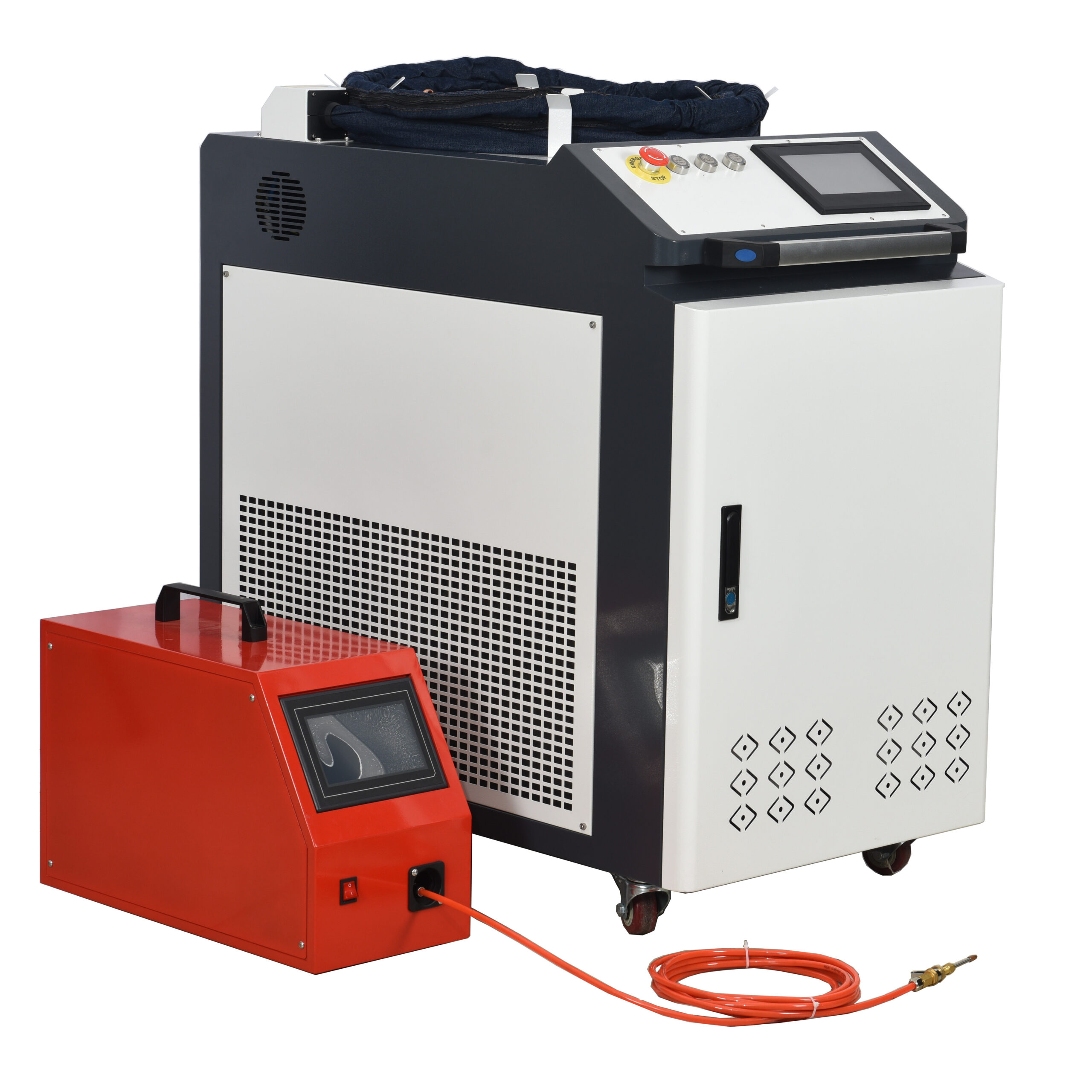





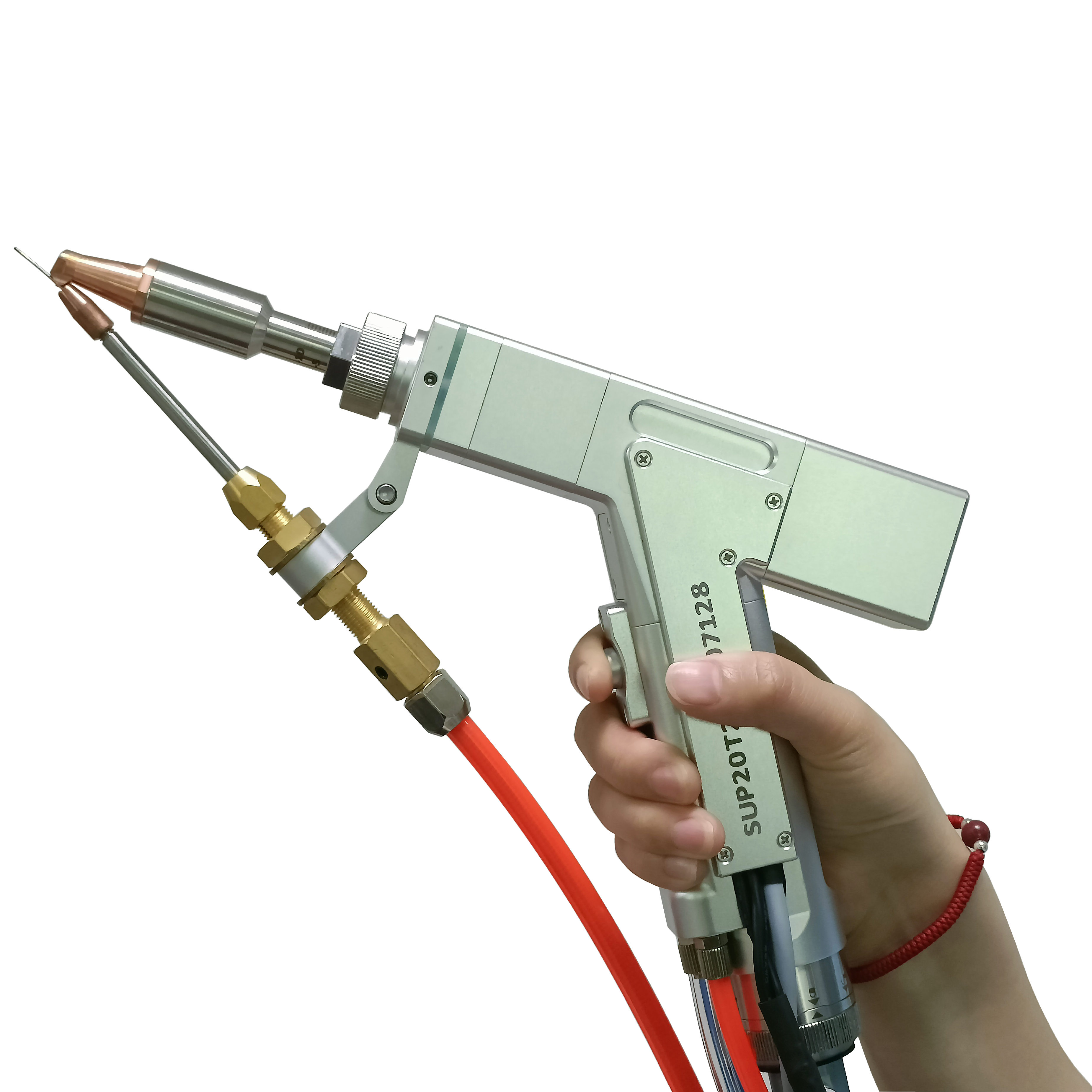




Handheld laser welding machine style selection
Product Introduction
- The handheld welding gun replaces the previous fixed light path, which is more flexible and convenient, enables long-distance laser welding, and overcomes the limitations of the workbench travel space;
- Red light positioning is used to calibrate the position of the welding head; the welding position is more accurate;
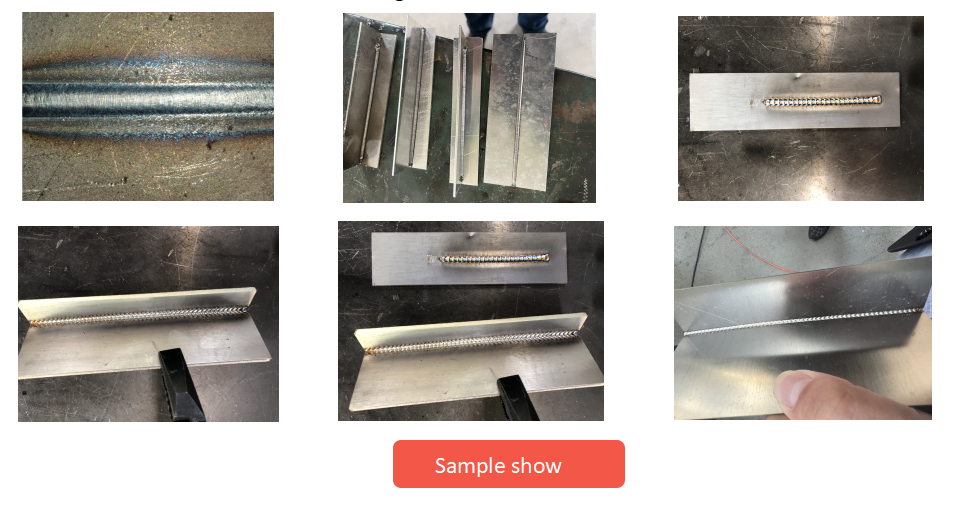
- The laser welding depth is large and the welding is firm;
- It is not easy to deform and is easy to grind and polish, which solves the problems of welding penetration, welding nodule and welding quality that occur when using argon arc welding;
- Used for various complex welds and spot welding of various devices.
Product Configuration
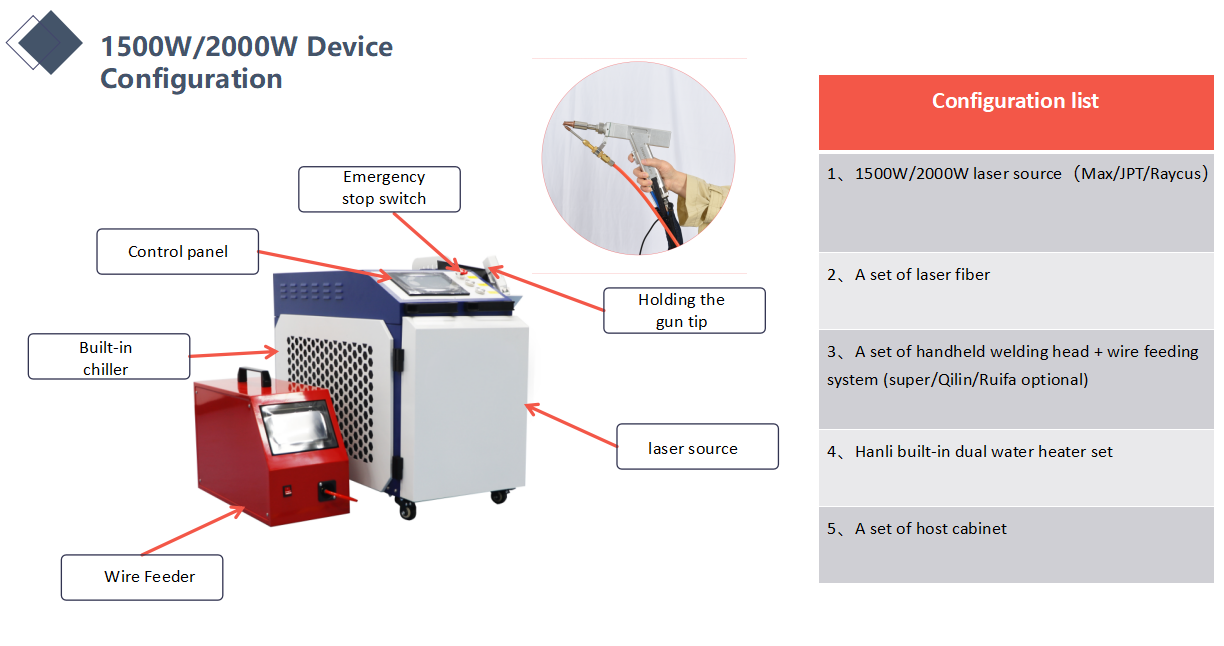
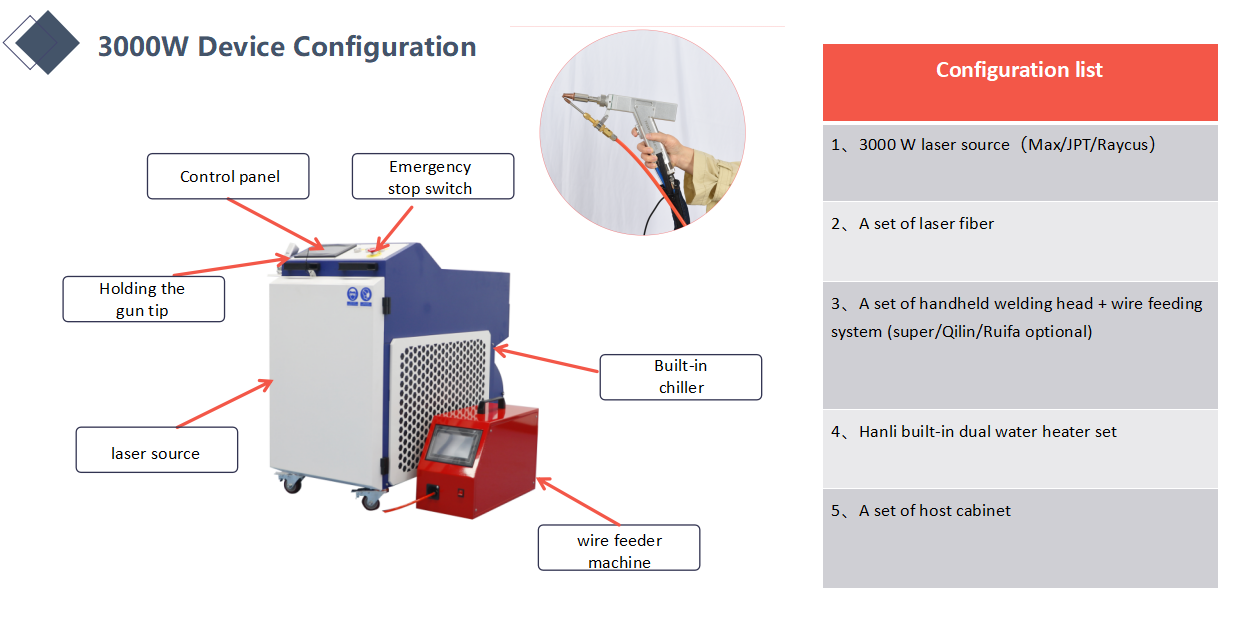
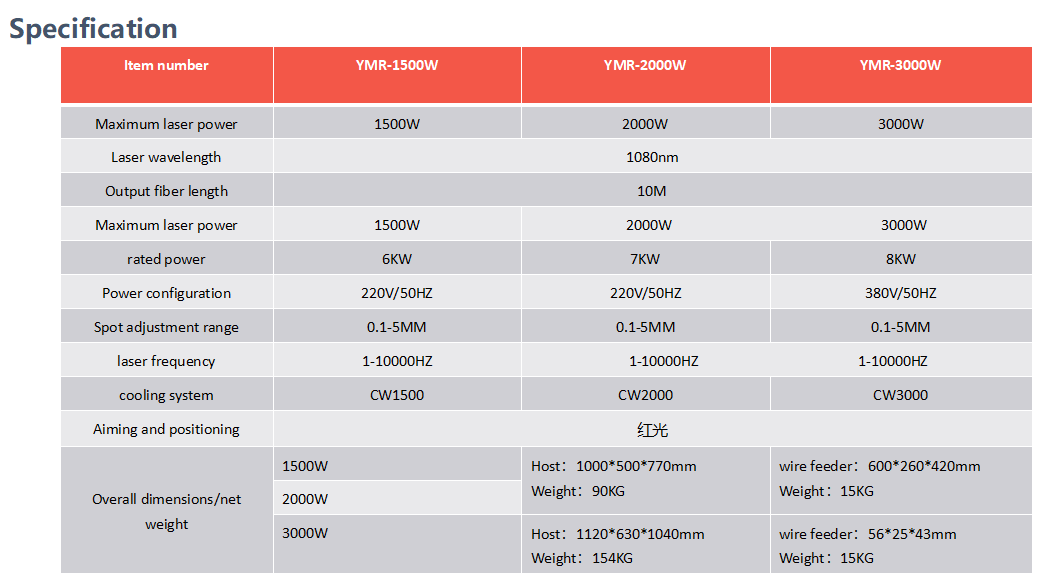
Product Parameters
Products Applications
Applications and Industries
The handheld fiber continuous laser welding machine is a versatile and efficient tool widely used across various industries due to its precision, flexibility, and high welding quality. It offers significant advantages in welding complex or large workpieces and is an ideal choice for small-batch production, repair work, and high-precision joining tasks. Below are the key application areas and industries that benefit from handheld fiber continuous laser welding machines:
1. Metal Fabrication and Sheet Metal Processing
- Application: Welding thin sheets, metal frames, and components.
- Materials: Stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, brass, and galvanized sheet metal.
- Benefits: Clean, aesthetic welds with minimal heat distortion, reducing the need for post-processing.
2. Automotive Industry
- Application: Repairing and joining automotive parts such as exhaust pipes, doors, fuel tanks, and fenders.
- Materials: Aluminum alloys, stainless steel, and high-strength steels.
- Benefits: Lightweight welding solutions with precise results, enhancing vehicle performance and safety.
3. Aerospace and Aviation
- Application: Fabrication and repair of components requiring high precision and strength, such as turbine blades and airframes.
- Materials: Titanium alloys, aluminum alloys, and stainless steel.
- Benefits: Ensures strong, reliable welds that meet strict aerospace standards.
4. Jewelry and Luxury Goods
- Application: Seamlessly joining or repairing intricate designs on jewelry, watches, and other fine metalwork.
- Materials: Gold, silver, platinum, titanium, and other precious metals.
- Benefits: Non-contact welding protects delicate designs and minimizes material waste.
5. Construction and Building Materials
- Application: Fabricating structural components, railings, window frames, and decorative panels.
- Materials: Steel, aluminum, and copper alloys.
- Benefits: Durable and aesthetic welds that withstand environmental stresses.
6. Kitchenware and Home Appliances
- Application: Joining parts for sinks, cookware, cabinets, and appliance housings.
- Materials: Stainless steel, aluminum, and galvanized steel.
- Benefits: Smooth, polished welds ideal for consumer-facing products.
7. Electronics Industry
- Application: Precision welding for electrical components, battery packs, and sensors.
- Materials: Copper, aluminum, and thin metal foils.
- Benefits: Reliable connections with minimal thermal impact on sensitive components.
8. Medical Devices
- Application: Manufacturing and repairing surgical instruments, medical implants, and diagnostic equipment.
- Materials: Stainless steel, titanium, and other biocompatible metals.
- Benefits: Hygienic and precise welds that meet stringent medical standards.
9. Furniture Manufacturing
- Application: Assembling and repairing metal furniture such as chairs, tables, and shelves.
- Materials: Steel, aluminum, and brass.
- Benefits: Durable and aesthetic welds that enhance product longevity.
10. Agriculture and Heavy Equipment
- Application: Repairing and fabricating parts for machinery, tools, and storage tanks.
- Materials: Carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum alloys.
- Benefits: High-strength welds that endure heavy-duty applications.